At some point in the middle of the last century, economics of money shifted to economics of psychology. When Milton Friedman wrote his 1963 book, A Monetary History, it was an effort that uncovered the role of money in the collapse of the Great Depression as he and his co-author, Anna Schwartz, saw it. Whether or not it was a full explanation, it wasn’t, it became widely adopted as the model for central bank behavior. At its heart, however, it was a treatise about the role of currency and liquidity.
It was still largely faithful to the Bagehot paradigm of central banks as agents of elasticity, with some modification about the terms at which that would be available. It is, however, nothing like what central banks around the world do today, even though outwardly there is a rough resemblance.
Almost as soon as A Monetary History was published there was a shift underway in more general economic theory about taking what was believed the next step – from monetary management to economic management. The impulse in that direction was not new, but the academy about its possibilities was. In 1958, AW Phillips in the UK put together an empirical analysis of a seeming durable correlation between inflation and employment. That was expanded in 1960 by Paul Samuelson and Robert Solow in the United States that posited the Phillips Curve, as it came to be known, as the means to exploit economic factors to introduce greater management and command.
Samuelson, in particular, was immediately welcomed into the Kennedy and then Johnson administrations as an advisor on the subject of that “exploitable Phillips Curve.” What we got out of it was the Great Inflation, a 15-year period of nearly unrelenting disaster that wasn’t just limited to economic malaise, it destroyed the last vestiges of the dollar and introduced the world to credit-based money in the eurodollar standard – the “dollar.”
Coming to terms with the Great Inflation was perfectly reasonable with a reasonable outlook free of determined bias for absolute control and command. Milton Friedman himself played a central role in discrediting the Phillips Curve, but that still left monetary theory short of the ancient Platonic ideal of the central banker as Philosopher King, if only in a limited capacity for creating and nurturing the “optimal” economic results. Despite the Great Inflation, economists did not turn away from trying to attain utopian command ideas, they only set about finding the “right” ones.
Robert Lucas was heavily invested in exactly that, as the allure of “general equilibrium” was so tantalizing to potential economic theory. It meant, as we know all too well now, that, if correct, there was some range of regression equations that could be assembled and constituted such that perfect predictability was possible. That is the idea of general equilibrium in the first place, to be able to model the utterly complex and heretofore mystifying nature of the true economy.
The world into which relatively primitive econometrics worked was centered around the idea of a “general equilibrium.” This was nothing new, as economists since the time of Malthus, Mill and Simon Newcomb believed that there was a method of quantifying any and all economic function. The equations would, as the name general equilibrium implies, have to balance. The central debate ranged around how price changes were set and modified especially owning to monetary and time variables.
What Lucas did, in his famous 1972 paper Expectations and the Neutrality of Money, was to assume generalized equilibrium from the very start. Departing from a regime of “adaptive expectations” Lucas asserted “rational expectations.” What that meant was neutralizing the equations of price expectations so that the difference between actual and expected prices is thus set to zero. In that sense, price behavior could then be adapted under a general equilibrium format, and the whole set of Freidman/Phelps “natural unemployment rate” econometrics would balance (I am simplifying here intentionally).
The generation of economists that undertook Lucas’ rational expectations assumptions saw its promise limited to the mathematical world of econometrics. The generation thereafter, including Ben Bernanke, sought to exploit it not unlike Samuelson and Solow’s attempt with Phillip’s scholarship. Rational expectations become the centerpoint of economic theory, and it has led the “discipline” in very strange directions.
The problem, as with quantum physics, is that “rational expectations” is not a real world phenomenon and certainly not directly relatable or transferable. It sounds as if it may be consistent with our experience of economic reality, as setting the differential of actual and expected prices to zero represents something like total market efficiency. It means that “market” prices are always correct and therefore econometric models need not concern themselves about initial equilibriums – they are always just assumed to be in that state. Inside the math, market prices are thus presupposed to always be market-clearing, and thus not subject to stochastic tests.
Even though the assumption of “rational expectations” is one in which there really appears to be no real-world counterpart, it dominates the centrality of all economic assumptions. Furthermore, like most economic and monetary paradigms, it is unfalsifiable. By adopting “rational expectations” at the start, any statistical tests are thus contained within the paradigm that all “market” prices are true and “correct.” That is a dangerous proposition when real world economic and financial parameters are supposed to flow solely from what is simply a means by which to find a solution within a system of stochastic equations describing only general equilibrium.
Because of this one mathematical property designed only to “save” general equilibrium largely from its own very real limitations, rational expectations has been taken as a real phenomenon to be abused in monetary policy, and thus economic command. If prices are always rational, then the influence of prices will be the same. Monetary policy left money behind and become strictly a tool for influencing behavior – from money and currency to nothing but psychology and the equivalent of happy pills (placebos at that).
We see the results of this shift all around us, especially where economists and “experts” are always so upbeat no matter how ludicrous and isolated such an attitude may be. And then there are the asset prices, going higher and higher to “stimulate” some “wealth effect” of not actual income but, again, happiness over not the direction of the true economy but of what its makers want of your perceptions of it all. It is taken as self-revealing now that even recessions are not much more than “irrational pessimism.”
The lack of recovery everywhere QE is being tried is not actually surprising to anyone but those still believing that rational expectations is anything but a mathematical shortcut. That is true in the US but most especially Japan, where even the mighty QQE has failed to live up to its “unquestionable” power and has thus become to engender very dangerous doubts – unhappy feelings that are the dread of all central bankers under the rational expectations paradigm:
While analysts expect consumption to pick up in coming months, lingering weakness will keep policymakers under pressure to underpin a fragile economic recovery.
“It’s a pretty gloomy number … Consumption may take longer than expected to pick up,” said Taro Saito, director of economic research at NLI Research Institute.
“The mood is good but wages haven’t risen much yet. It might take until around summer for consumption to clearly rebound.”
Reading that economist’s summary would lead you to think that it really is nothing but psychology at work. It is, after all, fully consistent with the stated purpose of QQE to begin with.
Households spent less on leisure and dining out even as the jobless rate fell to a 18-year low, underscoring the challenge of eradicating the sticky “deflationary mindset” that has beset Japan for nearly two decades.
If you think that Japan, or the US for that matter, is suffering from an insufficiency of happiness, a quarter-century funk of nothing but a “deflationary mindset”, then QQE seems a consistent course (never mind the nine prior attempts). If, however, you look at Japan as suffering just madness emanating from monetary policy that is the equivalent of pop psychology, the malaise starts to make perfect sense. The Japanese must be the happiest recipients of impoverishment ever conceived, and the results show. The greatest trick about rational expectations is that it seems so plausible because confidence is a good part of the real economy, but hollow appeals to unrelated factors are not in any way the same as “animal spirits.”
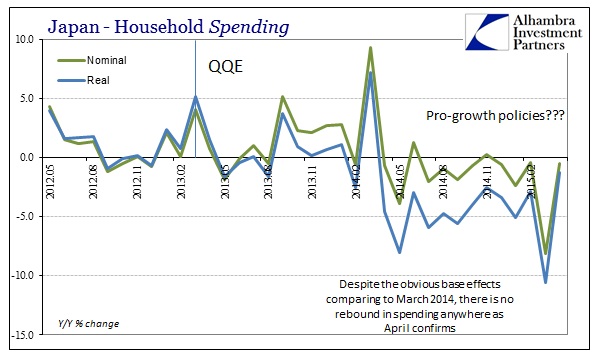
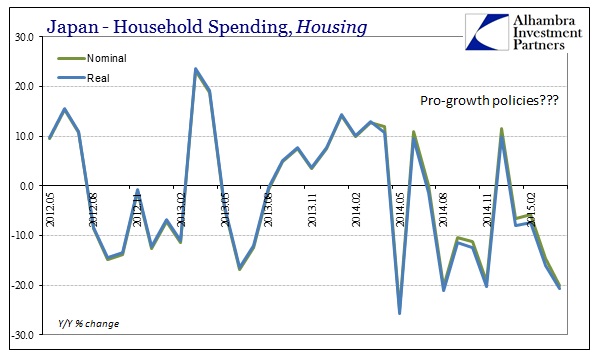
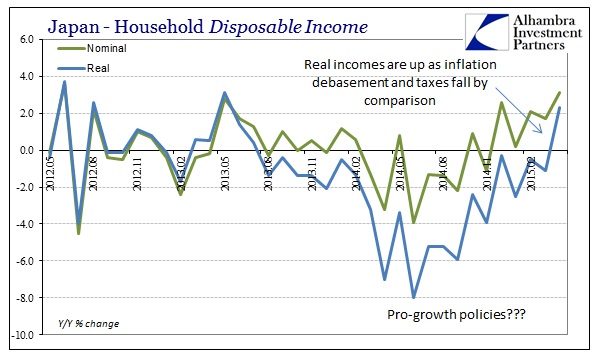
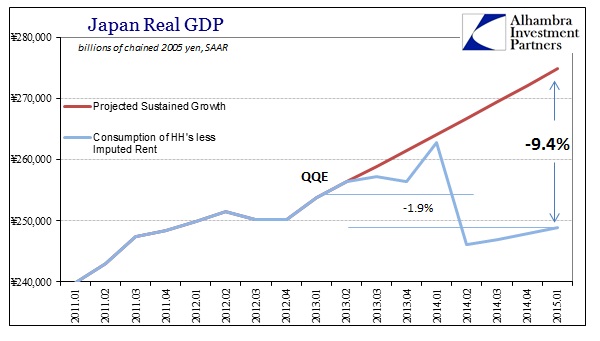
Last month was a difficult comparison because of the April 2014 tax change which pulled forward spending activity into March 2014, and thus the base of the year-over-year comparison was off. So it was expected that household spending would rise in April, with average expectations for +2.8%. Instead, spending declined yet once more, as economists missed their prediction by an enormous 4.1%. The problem with being reliant on illusions is that you can’t spend them; the Japanese, for all the ultra-low unemployment rate jubilee, have very little actual income. Even more recently, real DPI has ticked up but more as a matter of lower CPI and tax comparisons.
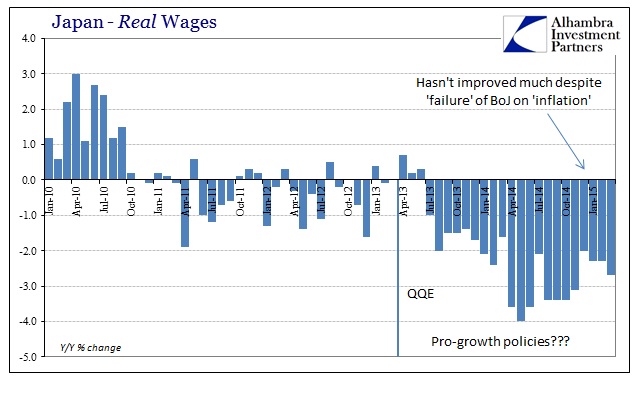
Instead, in what matters most, real wages have shown absolutely no tendency toward everything that was expected. When starting QQE more than two years ago, it was fully intended that by now real wages would not just be rising but rising steadily and robustly. Japanese workers have suffered the opposite.
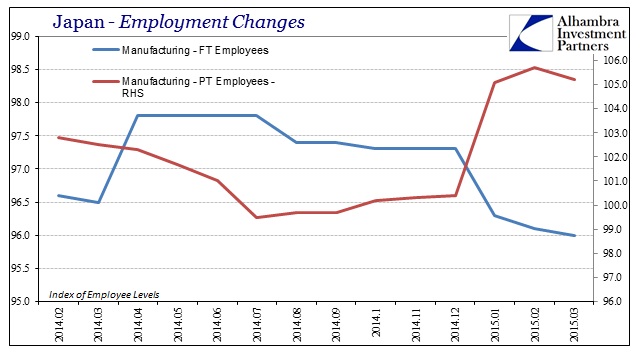
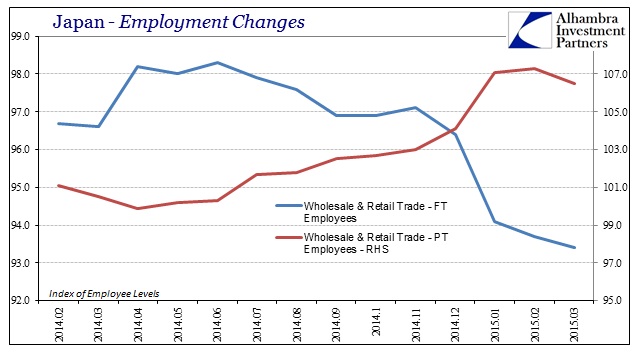
The reason for that is the very way in which the unemployment rate is misleadingly “happy”, connecting wages to what really looks like a still-gathering recession. In the past few months, when this post-tax recovery was supposed to materialize, Japanese businesses have been degrading their labor force, shifting a huge proportion at the margins out of full-time and into part-time. The Japanese still don’t do mass layoffs, instead they just cut hours strenuously while maintaining the “happy” unemployment rate.
I find it very revealing that this remaking of marginal labor utilization is largest in the wholesale and retail trade segments, further confirming the decimation of internal Japanese economics (in the truest sense, not the mathematical theories that dominate). The Japanese people are clearing buying less “stuff” meaning that those who sell stuff are requiring much less of workers in 2015. That is how recessions are made, in that they become self-feeding trends of reduced “demand” and then reduced labor utilization leading to further cuts in income and then demand again.
The problem for econometrics and rational expectations is that any scientific endeavor, and economics very much fancies itself as that, is governed by observation rather than academic stylings even of the most elegant and sophisticated math. Clear observation, now two full years into the emotional bastardization, rejects all conclusions and intentions of the orthodox theories right down to their base foundation. Yet, as noted by the quoted economist above, it will never be falsified by anything other than counter-emotion; rational expectations is so irrational in its persistence because it is no longer even a scientific-like pursuit but a full-blown ideology of religious fervor. No matter how back Japan gets, orthodox economists still say that recovery is later in the year, or next year, or just around some unspecified corner. And it never is; maybe not all prices, especially those highly managed and cajoled, are market-clearing?
The Japanese economy, to any clear mind, took a huge turn for the worst under Abenomics yet its practitioners are still, somehow, given the final word on judging its performance, meaning that the mainstream still, somehow, subscribes to the religion.
Spending by Japanese households slumped unexpectedly in April and consumer inflation came in roughly flat, casting doubt on the central bank’s view that a steady economic recovery will help move inflation toward its ambitious 2 percent target. [emphasis added]
By all scientific observation, there was nothing unexpected about the “gloom” in April.

Stay In Touch